 1.
You observe the spectrum of a star over several days.
1.
You observe the spectrum of a star over several days.
PHYSICS 406 - Introduction to Modern Astronomy
EXAM #3
April 10, 1996
Note: Each Question counts 2 points. 80 points correspond to 100 on the grade scale in the Syllabus.
Where you find the remark: (More than one answer), providing all correct answers leads to full credit. Only one correct answer leads to 1 point. Incorrect additional answer leads to subtraction of the first point.
 1.
You observe the spectrum of a star over several days.
1.
You observe the spectrum of a star over several days.
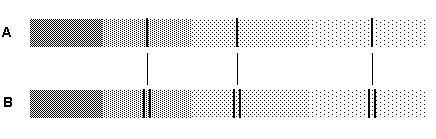
On the first day the spectrum behaves well and shows single lines for the elements (A). On the second day these lines seem to be split: one line is shifted towards blue and one towards red (B). On the third day the spectrum is similar to day 1, and on day 4 it is similar to day 2. What is the most likely reason for this behavior?
There must be 2 stars close to each other which orbit about each other such that on day 2 and 4 one of the stars moves towards us and the other away from us.
The star is pulsating. It is at rest on day 1, expanding on day 2, at rest on day 3 and shrinking on day 4.
The star is cooler on day 1 and hotter on day 2.
2. Which planets have rings? (Two for full credit. 3 or all 4 extra credit.)
Short answer
The "shepherd moon" will accelerate the debris such that it is swept away from the planet.
The "shepherd moon" will accelerate the debris just enough that it is lifted back into the ring.
The "shepherd moon" will decelerate the debris such that it falls down on to the planet.
The debris will collide with the "shepherd moon" and stick on it.
a star falling to Earth
a comet streaking across the sky
a distant nebula
a rock falling into the Earth's atmosphere
5. Where are most of the asteroids in the solar system?
in the Oort cloud
in the gap in the planet sequence between Mars and Jupiter
inside the orbit of Mercury
in orbit around the Earth
6. Refer to the following figure: In which direction does the plasma tail of the comet point? (Click the correct answer on the figure)
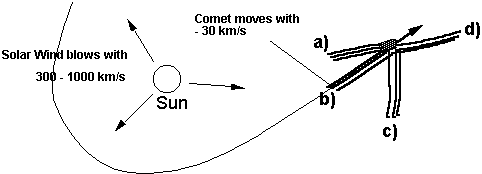
7. The dust tail of comets is formed in which way?
The comet head is running ahead of its own dust debris and therefore ahead of its dust tail.
Tidal forces during the passage of the sun tear dust out of the comet and pull a tail into the sunward direction.
Dust from the comet is driven away from the sun by solar radiation pressure and form a tail in the anti-sunward direction.
Dust will not form a comet tail.
8. How can a comet end? (More than one answer)
As a supernova.
It can break up into a meteor stream.
A comet can turn into a planet.
A comet may hit a planet or a moon.
|
|
|
|
|
9. When meteorite pieces were found, why was this so exciting for scientists?
The laws of gravitation could be studied from how fast the meteorites fell to the ground.
Until very recently meteorites were the only matter from outer space which could be studied in the laboratory.
The impact of meteorites produce most of the earthquakes.
Iridium is poisonous for dinosaurs.
Iridium is much more abundant in meteorites than in the Earth's crust.
Iridium is created in the melting of the Earth's crust during a meteorite impact.
Iridium is dug out of the Earth's interior during a meteorite impact.
11. The photosphere of the sun is
the region where the energy is produced
the layer of the sun from which most of the visible light comes
the hottest part of the sun's atmosphere
the sun's interior
the region filled with the solar wind
12. The Enterprise arrives at a star system with a blue star. The crew finds that the star has approximately the same size as the sun. What is the luminosity of this star like?
It is less luminous than the sun.
It has the same luminosity as the sun.
It is more luminous than the sun.
Can't tell, luminosity has nothing to do with colors.
13. What are the two elements that make up most of the material of the Sun?
Short answer
14. To determine the total energy flux from the sun we measure
the energy flux through 1 m2 at the distance of the Earth (which we know already)
the temperature on the Earth's surface
the size of the sun
the amount of light reflected from the moon
15. How do we know what the sun consists of?
from lines in the solar spectrum
from a spaceprobe we have sent into the sun
from the color of the sun's surface
from the shape of the sunspots
16. Which of the following is true? The solar energy captured by the Earth is
much more than the energy consumed by humans on Earth
just as much as the energy consumed by humans on Earth
much less than the energy consumed by humans on Earth
17. Why is a high temperature needed for energy production in the core of the Sun?
Hydrogen will not combine with oxygen at a low temperature.
Energy is needed to overcome electrical repulsion of hydrogen nuclei.
Electrons will not recombine at low temperatures.
The force of gravity is greater at high temperatures.
Speeds are less at high temperature, so there is more time for reactions between nuclei.
18. Name 2 possible ways to ionize neutral interstellar gas close to the sun. (all 3: extra credit)
Short answers
19. We know that the Sun's energy does not result from a chemical burning of coal. Why?
There is no ash on the bright surface of the sun.
There is no smoke coming out of the sun.
No carbon absorption lines are found in the sun's spectrum.
Even if the entire sun were made out of coal and oxygen, it would only have had energy for 10,000 years.
20. The bow shock of the Earth's magnetosphere is
a magic shield against Klingon weapons around the Earth
the supersonic boom of the Earth's magnetic field in the solar wind
the region where the aurorae originate
the region around the Earth where spacecraft usually reach supersonic speed when launched from the Earth
21. On the Earth we cannot control nuclear fusion yet, since we cannot contain the hot plasma which is needed for the reaction. What keeps the hot nuclear oven contained inside the sun?
electrical forces
the sun's magnetic field
the pressure resulting from the weight of material above
the centrifugal force from the sun's rotation
a Warp drive containment field
22. Granulation on the Sun's surface is a direct evidence of energy transport in the outer layers of the sun by
23. Which particles produced inside the sun in nuclear fusion are messengers which make their way directly to the Earth?
24. Helioseismology is
the measurement of pressure pulses of the solar wind
a theory which connects sunspots with earthquakes
the use of pulsations of the sun to gather information about its interior similar to using earthquakes
a theory to explain the dance of the planets around the sun
25. When an astronomer talks about a Blackbody she/he means
the same as a Black Hole
an object which does not reflect any light, but emits radiation due to its temperature
Batman at night
the night sky
26. The sunspots are darker than the surrounding regions because
they reflect less light
they contain the ash from the burning processes in the sun
they are cooler than the rest of the surface
they are hotter than the rest of the surface
they are holes in the solar surface
27. How do we know that the corona is has a temperature of 1-3 million degrees?
Because it is blue.
Spectral lines from highly ionized iron (lost many electrons) are observed in the corona
The corona is the brightest part of the sun
A spacecraft has been sent into the corona
28. To observe stars in the process of formation in the dusty interstellar clouds you should use
an X-ray telescope.
an ultraviolet telescope.
an infrared telescope.
29. If we obtain a spectrum from a bright nebula with interstellar gas we get
a continuous spectrum like from an incandescent body
a spectrum with bright lines
nothing, interstellar gas does not emit any light
30. If you were at "you are here" in the following figure, what would you see?
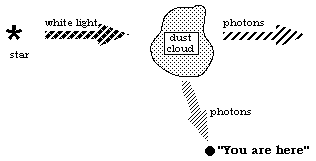
The star would look redder than it really is.
A blue reflection nebula.
Absorption lines produced by the dust particles.
A red interstellar gas cloud.
31. Assume a star with ten times the mass (i.e. ten times the fuel) of the sun. According to the Mass-Luminosity relation this star is about 3000 times as luminous as the sun. This star will
reach the same age as
live longer than the sun
live shorter than the sun
32. Stars are formed out of thin interstellar gas. Which of the following conditions are favorite for star formation? (More than one)
a high temperature of the gas
a fast rotation of the nebula
a low temperature of the gas
a strong magnetic field
a high density of the gas
a low density of the gas
|
|
|
|
|
33. You see two stars (A and B) in the sky that appear equally bright. From an astronomy book you learn that star A is 3 times as far away as star B.
What do you conclude about the luminosity of the two stars?
The luminosity of both stars is the same.
B is 9 times more luminous than A
B is 3 times more luminous than A
A is 9 times more luminous than B
A is 3 times more luminous than B
34. What is plotted on a Hertzsprung-Russell diagram?
Luminosity and temperature of stars.
Mass and size of stars.
Temperature and distance of stars.
35. Where on the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram below do you find the White Dwarfs? (Click the correct point on the image)
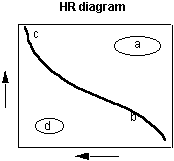
36. Where on the Main Sequence in the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram above (Figure in question 35) do you find the stars that live for the longest time?
|
|
|
|
|
|
37. A (cool) red giant star has the same luminosity as a (hot) blue giant. What can you conclude?
This cannot be true. One of the stars is cheating.
The red giant is the bigger star.
The blue giant is the bigger star.
Both stars have the same size.
38. The sun is shining so steadily because the pressure generated by heat from nuclear fusion in the sun's core is just balancing the weight of the material above. Imagine that by a fluctuation there is not enough heat generated for a short while. What happens in the sun's core?
The core will be compressed and therefore become hotter, which will increase the nuclear reactions again.
The core will shrink and the nuclear reactions will cease altogether.
The core will expand in order to re-ignite the nuclear reactions.
Heat will flow from the outer layers of the sun into the core to re-ignite the nuclear reactions.
39. The collapse of a gas cloud into star formation can be triggered by
a star passing through the cloud
a shock wave from a supernova compressing the cloud
magnetic forces
centrifugal forces
40. What is the reason that Population I stars have more heavy elements than Population II stars?
Population I stars are second generation stars and inherited the heavy elements from material processed already in earlier stars.
Population I stars are more massive than Population II stars.
Population II stars have lost all their heavy elements to their planets.
Population I stars have been bombarded with many meteorites which provided the heavy elements.
Population I stars have been treated by an alien spaceship with an any-ion beam.
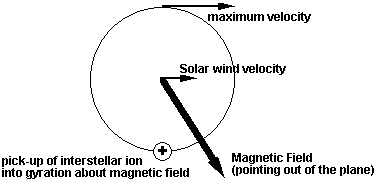 Bonus
Question 1: Refer to the drawing below. Close to
the sun, interstellar gas atoms loose one of their electrons and become ions.
Imagine a situation where the interplanetary magnetic field is perpendicular
(out of the plane in the drawing) to the solar wind while taken along with the
wind. Which velocities
can the interstellar ions gain from the solar wind and the magnetic field?
Bonus
Question 1: Refer to the drawing below. Close to
the sun, interstellar gas atoms loose one of their electrons and become ions.
Imagine a situation where the interplanetary magnetic field is perpendicular
(out of the plane in the drawing) to the solar wind while taken along with the
wind. Which velocities
can the interstellar ions gain from the solar wind and the magnetic field?
Interstellar ions are picked up with exactly the solar wind velocity.
Interstellar ions can reach up to twice the solar wind velocity after they are picked up.
Interstellar ions will only move along the magnetic field with their original velocity.
Interstellar ions won't move at all, because they are not influenced by the solar wind and the magnetic field.
Bonus Question 2: The hydrostatic equilibrium in the sun is maintained between
electrical forces and gravity
gas pressure and electrical forces
gas pressure and nuclear forces
gas pressure and the weight of material above