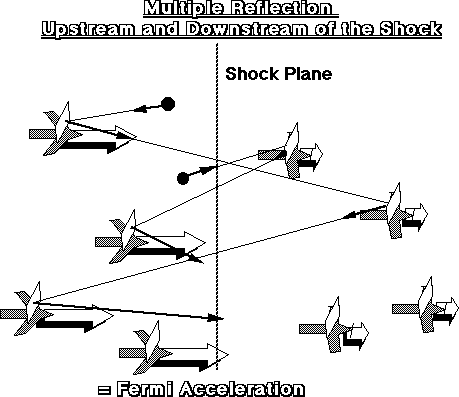
1. Boundary of the solar system
Solar wind is stopped by interstellar gas and plasma
| -> decelerated to sub-sonic speed | ||
| -> heliospheric termination shock | ||
| Ions accelerated at the shock: | like playing Ping Pong between the two sides | |

2. Interstellar gas in the solar system
For a general introduction to the Interstellar Medium see also this site.
a) Neutral gas enters the solar system
| from outside |
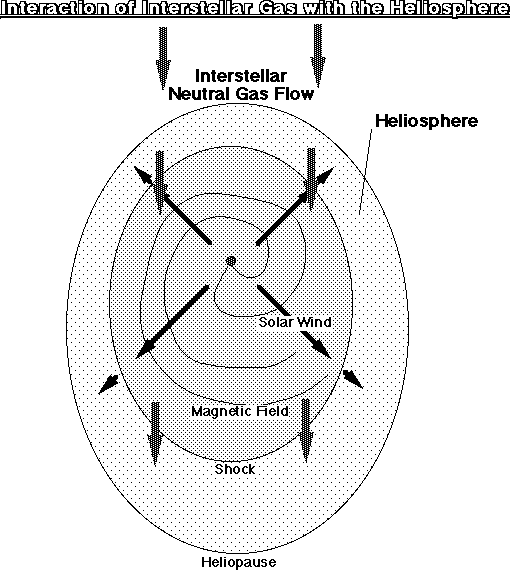
| b) Neutral gas is ionized | close to the sun | |
| by UV radiation | ||
| impact of solar wind ions | ||
| impact of solar wind electrons | ||
c) New ions will feel the magnetic field
| which is imbedded in the solar wind | |
| -> ions gyrate around magnetic (Giant Swing around field line) | |
| -> ions will be swept out of the system |
These ions have been measured!
| -> local information about the gas outside the solar system (interstellar gas) |
d) Sun moves with respect to the gas
| -> interstellar wind (like wind felt in cabrio) | |
To review the interaction of the interstellar gas with the solar wind you may want to view the the Movie "The Interstellar Gas Reveals Itself by the Giant Swing"
| Sun acts as gravitational lens | -> gas focused on the downwind side | |||
| Measure | Determine | |||
| absolute ion flux | -> density | |||
| density enhancement in focus | -> velocity and temperature | |||
| of interstellar gas | ||||
| a) absorbes light from stars | > observe dark lines in star spectra |
b) emits light
c) cold gas emits radio lines
21 cm line of un-ionized Hydrogen
| Importance: | lots of hydrogen in the universe; | ||
| spectral line | --> get velocity with Doppler effect | ||
| radio line | --> can see through dust (see below) | ||
Molecules:
| Cool clouds | --> molecules don't break apart when they collide | |
| Dense clouds | --> better chance for atoms to form molecules | |
| Cool and Dense | Þ Molecular clouds are "stellar nurseries" | |
a) Light scattering:
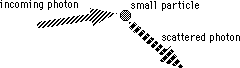
b) Obstruction (extinction).
c) Reddening:
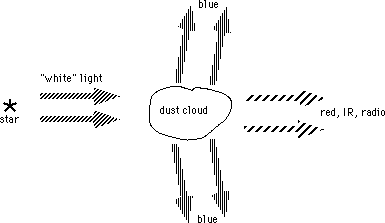
-> Radio & IR astronomy: see through dust clouds
d) Blue reflection nebulae
| Same physics in Earth's atmosphere | --> sunsets are red "Alpenglow"; sky is blue |
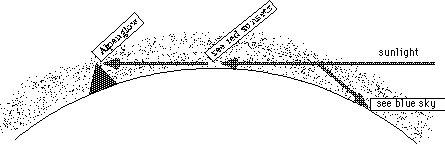
e) Why is there dust?
| Cool clouds | --> dust doesn't evaporate | |
| Dense clouds | --> more chance for molecules to come together |