Note: Each Question counts 2 points. 80 points correspond to 100%.
Where you find the remark: (More than one answer), providing all correct answers leads to full credit. One correct answer leads to 1 point. Second answer incorrect leads to subtraction of the first point.
1. What is 1.6 X 106?
2. To measure (for example, length, time, mass) means to ______________________ (short answer) it with a known (length, time, mass). Need help finding the answer? go here...... go to Q3
The model sun appears smaller because it is a smaller object
The model sun appears the same because both distance and size have shrunk by the same amount
The model sun appears larger than the real sun because it is closer
4. Saturn has about 10 times the radius of Earth. How much larger is its volume than that of Earth?
10 times larger
30 times larger
1000 times larger
100 times larger
I need to know the value of it to answer this question -
Short answer __________________________________________________ Need help finding the answer? go here...... go to Q6
the South Star is exactly at the horizon;
the sun passes exactly overhead;
the South Star is seen exactly overhead;
the stars move around you exactly parallel to the horizon.
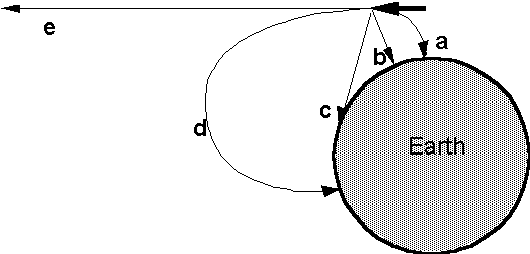
7. A space probe has been launched, and it is moving in the direction of the fat arrow. Suddenly the thrusters stop working at the position of the arrow. Which of the trajectories in the figure will the probe follow now? (Click on the letter in the image)
8. How did ancient Greek philosophers conclude that the Earth is a sphere?
The horizon looks like a full circle surrounding the observer.
The sky looks like a huge dome surrounding the Earth.
They noticed that the Earth's shadow on the Moon during a lunar eclipse is round.
They sailed around the Earth.
9. In Durham, NH, a star is observed to rise in the northeast. This star will be above the horizon
for only less than half a day
for exactly half a day
for more than half a day
I need to know which time of the year it is to answer this question
Short answer __________________________________________________ Need help finding the answer? go here...... go to Q11
11. The schematic below shows the sun as taken with multiple exposures of the sun during sunset close to fall equinox taken from your professor's high school. What is the geographic latitude of your professor's home town?
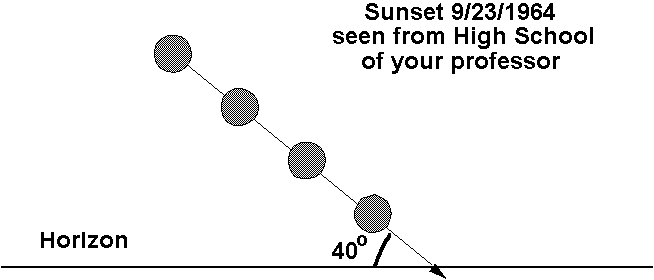
40 north
at the equator
50 north
50 south
The sun is not a good object to measure this because it changes its location in the sky over the year
Saturn's mass
Saturn's distance from the Earth
Saturn's rotation period
Saturn's distance from the Sun
13. 1 Astronomical Unit (1 AU) is
the size of a star;
the age of the universe
the distance of the Earth from the Sun
the distance of the Moon from the Earth
14. From which observation could Galileo deduce that the sun rotates?
Short answer _____________________________________________ Need help finding the answer? go here...... go to Q15
We compare it with a regular motion
We wait, till we feel enough time has elapsed
We cannot measure time
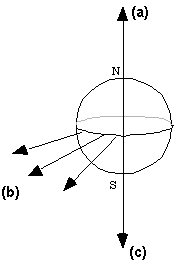
17. The figure below shows the Earth, with the Earth's North Pole (N) at the top. Which arrow points to the southern celestial pole? (Click on the answer within the figure)
Polaris will be lower in the sky than in NH
Polaris will be not be visible from Florida
Polaris will be higher in the sky than in NH
The Sun has grown larger.
The Sun is at a greater distance.
The Moon has shrunk.
The Moon is at a greater distance than usual.
This is called an ________________ Eclipse (1 Bonus Point) Need help finding the answer? go here...... go to Q20
high on the Meridian at midnight
in the western sky after sunset
in the eastern sky before sunrise
in the eastern sky after sunset
21. How did Copernicus explain the loops (retrograde motion) of the outer planets in the sky in his model of the solar system?
The planets move on epicycles.
The Earth passes the outer planets with a higher speed on its orbit around the sun.
The outer planets pass the Earth with a higher speed on their orbit around the sun.
The rotation of the planets about their axis produces the loops
22. On its orbit around the sun a planet
moves at higher speed when it is farther away from the Sun
moves at higher speed when it is closer to the Sun
does not change its speed at any time
moves backward on its orbit when it is in opposition
23. According to Kepler's 3rd Law the quantity
(Distance from the Sun)3/(Orbital Period)2 is
a constant for all planets in the solar system.
increasing with distance from the sun.
decreasing with distance from the sun
24. By using the detailed observations of Tycho Brahe about the motion of Mars, Kepler...
found that planets move exactly on circles around the Sun
confirmed that the planets orbit around the Earth
found that planets do not move on circles, but on ellipses
found that Tycho Brahe's observations were not exact enough to conclude anything.
The satellite pulls stronger on Earth than the Earth on the satellite.
The satellite is flying freely without a force acting on it.
The satellite pulls with the same force on Earth as the Earth on the satellite.
The Earth pulls stronger on the satellite than the satellite on Earth.
26. An object is in a straight motion and does not change its speed. What do you conclude?
A constant force keeps the object moving.
No force is involved to keep the object moving at the same pace.
You have to touch the object to draw a conclusion on whether there is a force involved or not.
27. The sidereal period of a planet is the time in which the planet completes one orbit with respect to the ___________________ (Short answer). Need help finding the answer? go here...... go to Q28
28. Refer to the following figure:
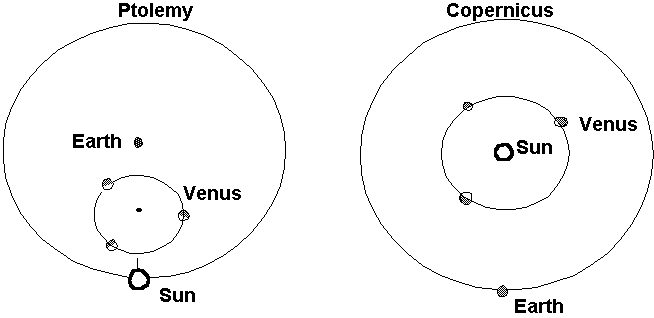
Which of the following phases are impossible to explain in the model by Ptolemy, but found in the model by Copernicus?
New and Crescent Venus
Half and Gibbous Venus
Crescent and Gibbous Venus
New and Half Venus
29. What was used to define the number of days in a week and their names?
The 7 bright stars of the Pleiades
Sun, Moon and the 5 planets that are visible without a telescope
The 7 planets up to Neptune excluding Earth
The 7 wonders of the world
30. The first astronauts on Mars will see the Earth moving in the Martian sky like we see from Earth
The inner (inferior) planets
The outer (superior) planets
The Moon
It is not possible to see the Earth from Mars.
31. A lunar eclipse occurs on April 3. When will be the next opportunity for a lunar eclipse?
About 3 months later
About 6 months later
About 9 months later
About 1 month later.
one degree.
one-half degree.
one-quarter degree.
33. Why don't eclipses occur at every new or full Moon?
The Moon's orbital plane is inclined 5 degrees from the Earth's orbital plane.
There is an eclipse at every new or full moon, but they are only visible from special places on the Earth.
Eclipses only occur when the Moon is closest to the Earth.
34. Mars is close to Opposition. Where do you find Mars shortly after sunset.
low in the western sky
high in the sky in the south
close to Polaris
low in the eastern sky
changes the speed and mass of an object
changes the mass and does not influence the motion of objects
changes the direction of motion and the speed of an object
changes the mass and the direction of motion of objects
36. The seasons on Earth come from the fact that
Earth is farther away from the Sun in winter than in summer
Earth's axis is tilted with respect to the axis of the Earth's orbit around the Sun
the Sun emits less light in winter than in summer
The star will just rise in NH
This star will not be visible from NH
This star will be exactly overhead
The star will just set in NH.
38. The constellation of Orion is
only visible from locations in the southern hemisphere
only visible around midnight
always visible in the sky over Durham
rising exactly in the East and setting exactly in the West.
39. It is waning half Moon. Where do you look for the Moon shortly after midnight?
I would not see the Moon at this time.
The Moon will just be rising in the East.
The Moon will almost be setting in the West.
The Moon will be high in the sky in the South.
The answer depends on the time of the year.
40. From the southern hemisphere of Earth the planets are seen
crossing the sky in its northern part
crossing the sky in its southern part as here
never.
From where on Earth are we able to see only half of the entire sky, no matter how long we are watching?
We can see all stars from any point on Earth. We only have to wait through an entire year to be able to see all stars.
We can see only half the sky on the equator, because it cuts the sky exactly into a northern and a southern half.
On one of the poles we can only see half the sky, because none of the stars ever rises or sets here.
There is no such place on Earth. We can always see more than half of the sky, because the apparent rotation of the sky brings other constellations into sight.
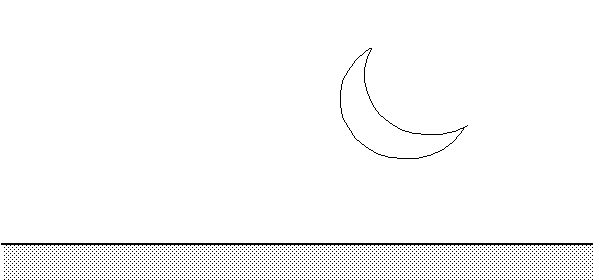
You are somewhere in NH. From the way the situation looks like you can derive into which general direction you are looking. Which answer is correct?
West
South
North
East.
This is a ________________________ (short answer) crescent Moon. 1 Bonus Point Need help finding the answer? go here...... go to NEXT BONUS Q
Reserve Questions:
xx. From the appearance of the phases of the Moon the Greeks reasoned that the Moon is _________________ (Short answer). Need help finding the answer? go here......
xx. The method by which we can derive something that we cannot directly measure from measurements of other quantities is called: